The Vuber Earth Initiative
Batteries have become an integral necessity for people to function in today’s modern digital world; they've been integrated into our daily lives since their invention in the late 1970s. Today, lithium ion batteries come in a variety of sizes and can be found in nearly every household; laptops, cell phones, flashlights, and many other handheld devices rely on these power sources to function. Most batteries aren’t rechargeable, meaning they’re single use and often get improperly disposed of by being thrown away with other household trash. When batteries get thrown in the garbage, they end up in a landfill where dire consequences are imminent. Unfortunately it’s estimated that only 5% of the world’s lithium ion batteries end up being recycled. As a battery company, Vuber recognized the role they were playing by providing consumers with a battery powered device that isn’t easily recyclable which is how the Vuber Earth initiative was started. This program aims to create a battery stewardship program for their batteries and cannabis disposables.
Fire Hazards

The United States estimates that 3 billion batteries are thrown away into our landfills each year which causes a plethora of issues. Lithium ion batteries are composed of an anode, cathode, electrolyte, a separator, and positive/negative collector. These components are made up of graphite, lithium, cobalt, and manganese which can have dangerous outcomes when exposed to the environment. Fires caused by Li batteries are very dangerous because they contain a flammable electrolyte and significant stored energy. When the battery is unable to disperse the stored energy it overheats, causing thermal runaway - a process in which a series of exothermic reactions creates excess heat that can catch itself or nearby materials on fire, in some instances an explosion can occur. These fires aren’t easy to put out since it creates its own source of oxygen and the fumes leaving the battery are also toxic and flammable. To put it in perspective, a regular vehicle fire will take a couple hundred gallons to extinguish, an electric vehicle that caught on fire in Texas needed over 30,000 gallons and 4 hours to extinguish the flames. A special type of fire extinguisher has been developed to extinguish lithium battery fires since their appearance has become more prevalent in recent years. In 2022, New York alone had reported 220 lithium ion related fires that ended up killing 6 people and injured 147. Of course, not all of these fires occur in the landfills but when they do they present an avoidable challenge and substantial risk to the waste disposal industry.
The Environmental Impact
The law of conservation tells us that matter cannot be created nor destroyed, only changed. This tells us that the resources on Earth are limited and finite, the amount of lithium that we started with is all we’ll have access to on this planet. It’s a shame that we are throwing our precious resources away to an area that will be difficult to reclaim. It’s estimated that the earth contains roughly 88 million tonnes of lithium, however, only a quarter of this is available to be mined and commercially used. It’s predicted that we will have more access to this resource as our technology improves but this doesn’t seem like a good solution. Instead, people should be trying to recycle the materials that we already have.
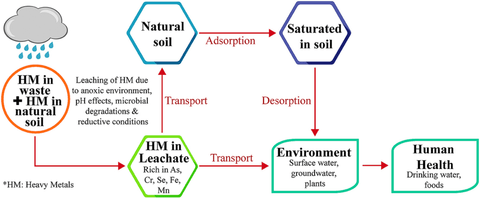
When batteries make their way to the dump, they often get compressed by various machines and buried in the dirt, which can crack/expose the insides of a battery. Overtime, the precious metals will begin to leach into the surrounding environment which affects all aspects of the ecosystem. Leaching starts in the soil but will eventually make its way into the water cycle where it will be recycled and dispersed throughout the environment. This contaminated water can end up in our aquifers where people will unknowingly consume heavy metals through drinking water from their tap. Soil contaminated by heavy metals will likely affect the plants that soak up the nutrients from its surrounding areas. Not only will this kill the plants, but it could also be a transport vessel into the bodies of animals that eat those plants.
Government Intervention
Over recent years, federal and state governments have started to recognize the dangers associated with improper lithium battery disposal. A study conducted by the Environmental Protection Agency found that there have been over 245 fires caused by lithium ion batteries in landfills, garbage trucks, or other waste facilities over the past decade. These fires prompted governing bodies to take action by banning improper battery disposal, allocating funds for battery stewardship programs, and holding companies accountable to recycle their products that utilize these products. Nineteen states have enacted battery recycling laws, 10 states also require battery producing companies to fund or offer a recycling program.
Recently, there have been a lot of laws passed regarding lithium ion batteries in Vuber’s home state of Washington. In 2023, Washington passed a law that would require battery companies or companies whose products contain batteries to develop a program to recycle their products by 2027. On top of this, Seattle also passed a ban on the improper disposal of any batteries within the city. After speaking with Seattle Public Utilities, it has been determined that cannabis disposables are included in this ban.
With only 5% of the United State’s battery supply being recycled, it’s no surprise that the government is taking steps to retain the lithium supply that’s currently in circulation. The US has allocated billions of dollars towards battery stewardship programs in an effort to stop outsourcing from other countries. With electric vehicles rising in popularity, the states wants to bring business back into a circular economy such that we produce and sell our own products. This effort started years ago, however, its predicted that the US won’t be able to produce half of the EV batteries that we’ll need by 2028. Currently most of the world's batteries come from Korea, China, Australia, and Chile.
Vuber Earth Initiative

Vuber recognizes the lithium ion waste that the cannabis industry produces through cannabis batteries and disposables. With disposables taking over the market, it is as crucial as ever to address the excessive waste from these products. This is why the Vuber Earth initiative was created - to approach a problem that has been largely ignored by consumers and producers. We’ve developed a recycling program for our batteries through our website that allows customers and clients to recycle their broken/used Vuber batteries, so far, we’ve recycled over two thousand batteries in house. We don’t want to stop here, we are working on expanding our recycling program across the state by implementing a cannabis battery stewardship program for Washington with hopes of eventually reaching California and Oregon. Our proposed stewardship would include drop off boxes at partnered locations, allowing consumers to easily and safely dispose of their used disposables/batteries. Since these products contain some amount of cannabis, there have been many restrictions surrounding the project. Conflicting answers from various government entities have halted significant progress towards implementation. However, with the new battery ban in Seattle, we are hopeful that we will be able to start a pilot program there soon. Vuber will continue to strive in all aspects of innovation throughout their business.




















